What is an Airplane Transponder? How It Works & Why It Matters
Understanding airplane transponders is crucial for anyone involved in aviation. These devices are essential for safe and organized air travel, facilitating communication between pilots and air traffic control (ATC). This communication allows controllers to track aircraft precisely, ensuring safe separation and efficient traffic flow.
This article will explore what a transponder is, its functions, how it enhances aviation safety, and the regulations surrounding its use. By understanding this vital piece of avionics equipment, pilots and aviation enthusiasts alike gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of modern air travel.

What is an Airplane Transponder?
An aircraft transponder, short for "transmitter responder," is a crucial piece of aviation equipment that enhances safety and efficiency in air traffic management. Acting as a communication bridge between an aircraft and Air Traffic Control (ATC), the transponder allows controllers to identify and track aircraft on their radar screens.
Its primary function is to transmit information about the aircraft's identity and altitude, enabling ATC to maintain safe separation between aircraft and provide essential guidance during flight. This vital communication helps ensure smooth and organized air traffic flow.
How a Transponder Works: Understanding Modes and Codes
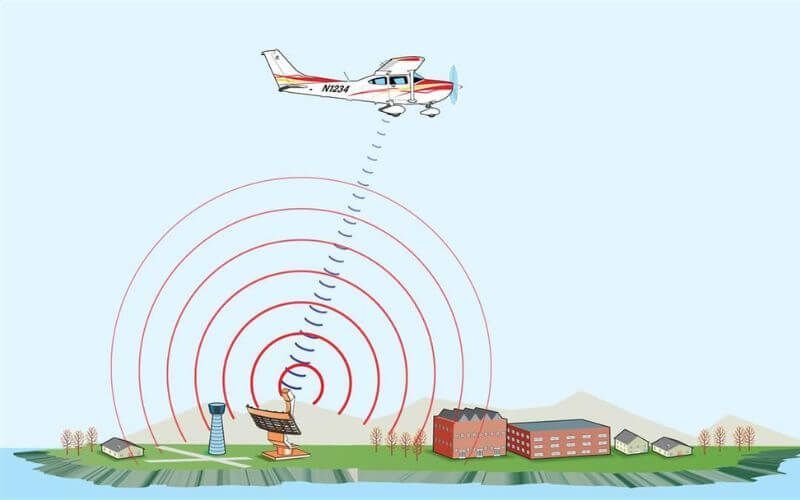
A transponder operates on an interrogation/response principle. ATC radar sends out interrogation signals, which the aircraft's transponder receives and responds to by transmitting specific data.
This data is displayed on the ATC radar screen, providing vital information about the aircraft. Different modes determine the type of information transmitted. Mode A provides a 4-digit identification code (squawk code) assigned by ATC, allowing controllers to distinguish each aircraft. Mode C automatically transmits the aircraft's altitude, enhancing situational awareness for ATC.
The more advanced Mode S, alongside providing identification and altitude, facilitates data exchange for enhanced surveillance and collision avoidance systems like ADS-B. ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) utilizes Mode S transponders to broadcast aircraft information, including position, velocity, and altitude, to ground stations and other equipped aircraft, further enhancing safety and efficiency.
Types of Airplane Transponders & Their Applications
Aircraft transponders are categorized into active and passive types, each with distinct operational characteristics and applications. Active transponders, the most common type in modern aviation, generate their own radio frequency signals in response to interrogation signals from ATC radar.
They offer increased range and accuracy, making them essential for air traffic control. Passive transponders, on the other hand, rely on reflected radar signals and don't generate their own signals. While simpler and less expensive, they have limited range and are less accurate than active transponders. They are typically found in smaller aircraft or for specific applications where the enhanced capabilities of an active transponder are not required.

Setting and Using a Transponder in Flight
Pilots set their transponder's squawk code, a four-digit identification number assigned by ATC, using either manual knobs or digital interfaces depending on the aircraft's equipment. With manual knobs, each digit is selected individually. Digital systems offer a keypad or touchscreen input, often with error-checking features.
Pilots exercise careful attention to detail when entering codes to avoid inaccuracies. Transponders are typically enabled and disabled with a dedicated switch. Many modern aircraft feature automatic activation systems linked to specific phases of flight, ensuring the transponder is active when necessary. Proper training and adherence to procedures are crucial for pilots to correctly operate and utilize transponders effectively.

Importance of Transponders for Aviation Safety
Transponders are indispensable for aviation safety, playing a vital role in maintaining order and preventing accidents in the increasingly complex airspace. By providing a clear and reliable means of aircraft identification and altitude reporting, they allow Air Traffic Control to manage traffic flow efficiently, ensuring safe separation between aircraft.
This accurate and real-time information is crucial for collision avoidance systems, enabling pilots and controllers to take preventative actions. Furthermore, in emergency situations, transponders greatly assist search and rescue operations by enabling quick and precise location of aircraft in distress. The benefits of transponders extend beyond routine operations, contributing significantly to the overall safety and security of the aviation system.
Transponder Regulations and Airspace Requirements
Transponder usage is governed by strict regulations set forth by international and national aviation authorities, including the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and, within Australia, Airservices Australia.
These regulations mandate transponder use in specific airspace classifications and under certain flight conditions. Pilots must understand and adhere to these regulations. Key transponder codes include 1200 for VFR flights, 7600 to indicate radio failure, and 7700 for emergencies.
The Mode C veil, an area surrounding busy airports, requires aircraft to have an operating Mode C transponder to provide altitude information for enhanced safety. While Class G airspace generally doesn't mandate transponder use, specific areas within it may require them, highlighting the importance of pilots checking airspace requirements before each flight. Compliance with these regulations is essential for safe and efficient air traffic management.
FAQs about Airplane Transponders
What is the difference between Mode A, Mode C, and Mode S transponders?
Mode A transponders provide a 4-digit identification code (squawk code) assigned by ATC, allowing controllers to distinguish each aircraft on their radar screens. Mode C adds automatic altitude reporting to the identification, enhancing situational awareness for air traffic controllers.
This altitude information is crucial for maintaining safe vertical separation between aircraft. Mode S, the most advanced type, provides not only identification and altitude but also facilitates data exchange for enhanced surveillance and collision avoidance systems. This includes aircraft-specific information like airspeed and heading, allowing for more precise tracking.
These different modes contribute to a layered system of information sharing, improving the efficiency and safety of air traffic management.
Is a transponder required for all flights?
Transponder requirements vary based on airspace classification and flight rules. In controlled airspace, particularly around busy airports, transponders are generally mandatory. This allows ATC to positively identify and track aircraft, ensuring safe separation and efficient traffic flow.
For Visual Flight Rules (VFR) flights in uncontrolled airspace, transponders may not be strictly required in some areas, although their use is highly recommended for enhanced safety and visibility to other aircraft.
Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) flights, regardless of airspace, always require an operating transponder. Pilots should consult relevant aviation regulations and charts to determine the specific transponder requirements for their planned flight route and airspace.
What should I do if my transponder fails during flight?
If your transponder fails during flight, it's crucial to remain calm and follow established procedures. First, attempt to troubleshoot the issue if possible, checking circuit breakers and connections. If the problem persists, switch your transponder code to 7600, the international code for radio failure. This alerts ATC to your situation. Then, attempt to contact ATC on the assigned frequency or an appropriate emergency frequency.
If unable to establish radio communication, follow established lost communication procedures for the relevant airspace. These procedures typically involve squawking 7600 and adhering to specific altitude and routing instructions for the area.
How do I set a squawk code correctly?
Setting a squawk code accurately is essential for proper identification by ATC. With manual knobs, rotate each knob individually to select the assigned digits. Double-check each digit after setting it to avoid errors.
On digital systems, enter the code using the keypad or touchscreen interface. These systems often feature error-checking functionalities, providing an additional layer of assurance.
Regardless of the method used, confirm the entered code with the ATC instructions to ensure accuracy. Careful attention to detail and clear communication with ATC are crucial for proper transponder operation.
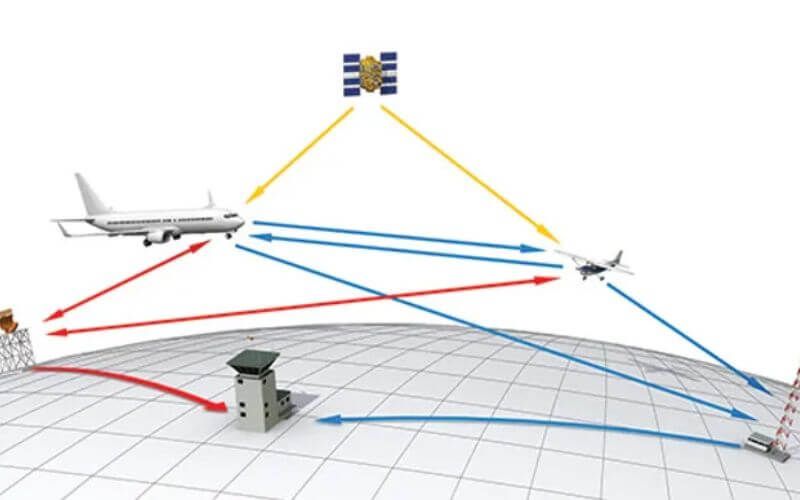
What is ADS-B and how does it relate to transponders?
ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) is a technology that enhances aircraft surveillance by automatically transmitting aircraft position, velocity, and other data. Unlike traditional radar, which relies on ground-based systems, ADS-B broadcasts information directly from the aircraft.
ADS-B Out utilizes Mode S transponders to transmit data to ground stations and other equipped aircraft, improving situational awareness and enabling more precise tracking. ADS-B In allows aircraft to receive data broadcasts from other aircraft and ground stations, enhancing collision avoidance capabilities and providing real-time weather and traffic information.
The integration of ADS-B with Mode S transponders represents a significant advancement in aviation safety, promoting more accurate and comprehensive surveillance, especially in areas with limited radar coverage.
Gojets - Providing Services for Your Transponder Needs
GoJets understands the critical role transponders play in aviation safety and efficiency. Our team of experts possesses extensive knowledge of various transponder systems and can provide tailored advice to clients regarding the best options for their specific aircraft and operational needs.
Whether you're looking to upgrade your existing transponder, install a new system, or ensure compliance with current regulations, GoJets offers comprehensive support. We assist with transponder installation, maintenance, and certification, ensuring your aircraft meets all regulatory requirements.
For clients looking to acquire aircraft equipped with advanced transponder technology, including ADS-B capabilities, we offer a range of aircraft sales and fractional ownership programs. These programs provide access to modern aircraft with the latest avionics, ensuring optimal safety and compliance.
To learn more about how GoJets can meet your transponder needs, visit our website at
- Phone number: 0401036356
- Website: https://gojets.com.au/

Transponders are fundamental to modern aviation, serving as essential tools for enhancing safety, efficiency, and communication in the skies. From ensuring safe separation between aircraft to aiding in search and rescue efforts, their importance is undeniable.
Understanding the different types of transponders, their functionalities, and the relevant regulations is crucial for all pilots and aircraft owners. This knowledge empowers informed decisions regarding equipment selection, operation, and compliance. For expert advice and










